การจัดการภาวะโพแทสเซียมในเลือดต่ำจากยา Amphotericin-B deoxycholate : รายงานกรณีศึกษาผู้ป่วย 1 ราย
คำสำคัญ:
เชื้อราคริปโตคอคคัส, โพแทสเซียมในเลือดต่ำ, การทดแทนโพแทสเซียมบทคัดย่อ
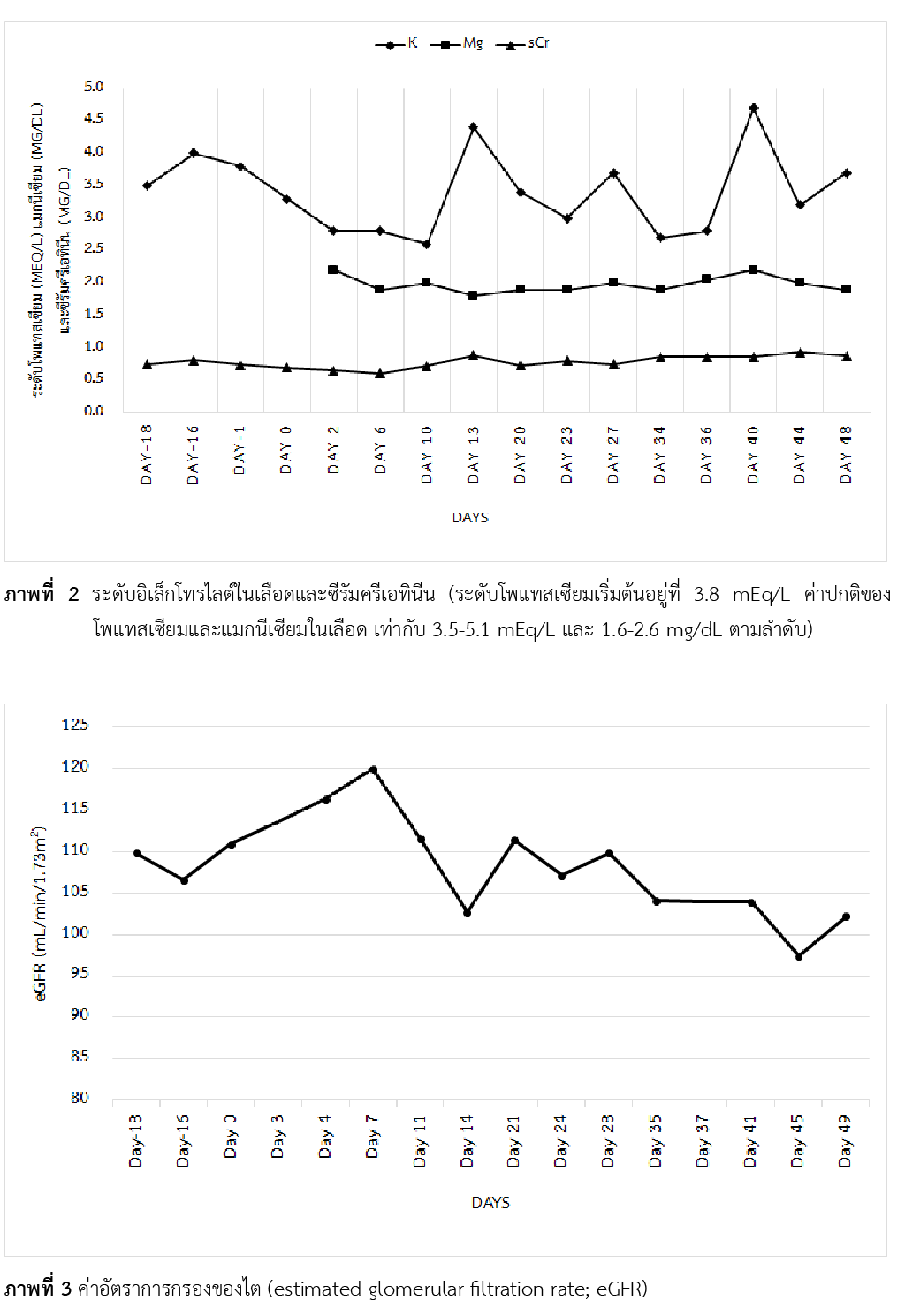
Amphotericin B deoxycholate (AmB-d) เป็นยาทางเลือกแรกสำหรับรักษาเยื่อหุ้มสมองอักเสบจากเชื้อราคริปโตคอคคัส (cryptococcal meningitis) ทั้งในผู้ป่วยภูมิคุ้มกันปกติหรือภูมิคุ้มกันบกพร่อง อาการไม่พึงประสงค์จากยาที่พบบ่อย ได้แก่ ภาวะไตบาดเจ็บเฉียบพลัน (acute kidney injury) และอิเล็กโทรไลต์ไม่สมดุลโดยเฉพาะภาวะโพแทสเซียมในเลือดต่ำ (hypokalemia) ซึ่งสามารถป้องกันหรือลดความรุนแรงได้ด้วยการให้สารน้ำและอิเล็กโทรไลต์อย่างเพียงพอ โพแทสเซียมในเลือดต่ำอาจนำไปสู่ภาวะแทรกซ้อนที่รุนแรงต่อระบบหัวใจและกล้ามเนื้อ ปี พ.ศ. 2561 องค์การอนามัยโลกแนะนำการให้สารน้ำ (prehydration) ก่อนบริหารยา AmB-d และการทดแทนโพแทสเซียมตั้งแต่ช่วงแรกของบริหารยา AmB-d แต่การศึกษาทางคลินิกของการทดแทนโพแทสเซียมในช่วงแรกของการให้ AmB-d ยังมีอยู่จำกัดจึงยังไม่เป็นที่ยอมรับในวงกว้าง รายงานฉบับนี้แสดงกรณีศึกษาผู้ป่วยชายไทย อายุ 46 ปี มาโรงพยาบาลด้วยอาการพูดไม่ชัด ปวดศีรษะ เห็นภาพซ้อน ไม่ได้ประสบอุบัติเหตุ ปฏิเสธโรคประจำตัว ทำงานอยู่ในโรงเลื่อยไม้เป็นเวลา 10 ปี ผลสแกนสมองไม่มีหลักฐานของภาวะเส้นเลือดในสมองตีบหรือเลือดออกในสมอง ผลตรวจ cryptococcal antigen titer เป็นบวก แพทย์วินิจฉัยการติดเชื้อราคริปโตคอคคัสในเยื่อหุ้มสมอง จึงเริ่มรักษาด้วย AmB-d ร่วมกับ flucytosine ผู้ป่วยได้รับโพแทสเซียมรูปแบบรับประทานเสริมตั้งแต่ช่วงแรกของการใช้ยา AmB-d ต่อเนื่องจนกระทั่งระดับโพแทสเซียมเป็นปกติ
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Perfect JR. Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s principles and practice of infectious diseases. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2015. 2934–48.
พิไลพันธ์ พุธวัฒนะ. เอซไอวีและจุลชีพฉวยโอกาส. กรุงเทพฯ: อักษรสมัย; 2541.
ภัทรกร บุบผัน, อภิสรา โสมทัศน์, พรสวรรค์ จินพุทธ, ณัฐชาติ ประมงคล, อนุกูล ศรีธวัชพงศ์. การตรวจหาเชื้อรา Cryptococcus neoformans จากมูลนกภายในบริเวณมหาวิทยาลัยศรีนครินทรวิโรฒ องครักษ์. วารสารมหาวิทยาลัยศรีนครินทรวิโรฒ (สาขาวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี) 2017;9(18):128-35.
ศมนีย์ ศุขรุ่งเรือง. เชื้อราก่อโรคและโรคเชื้อรา. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1. กรุงเทพฯ: ภาควิชาจุลชีววิทยาคลินิก คณะเทคนิคการแพทย์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล; 2529.
Zimmer BL, Hempel HO, Goodman NL. Pathogenicity of basidiospores of Filobiasidiella neofomans. Mycothathologia. 1984;85:149-53. doi: 10.1007/BF00440944. PMID: 6738667.
Sukroongreung S, Kitiniyom K, Nilakul C, Tan–timavanich S. Pathogenicity of basidiospores of Filobasidiella neoformans var. neoformans. Med Mycol. 1998;36(6):419-24. PMID: 10206753.
Pappas PG. Cryptococcal infections in non-HIV-infected patients. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2013;124:61-79. PMID: 23874010.
John RP, William ED, Francoise D, David LG, John RG, Richard JH, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of cryptococcal disease: 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(3):291-322. doi: 10.1086/649858. PMID: 20047480.
Beardsley J, Sorrell TC, Chen SC. Central ner–vous system cryptococcal infections in non-HIV infected patients. J Fungi. 2019;5(3):71. doi: 10.3390/jof5030071. PMID: 31382367.
ศิริลักษณ์ อนันต์ณัฐศิริ. Amphotericin B: antifungus. ใน: นลินี อัศวโภคี, ธีระพงษ์ ตัณฑวิเชียร, ธนะพันธ์ พิบูลย์บรรณกิจ, บรรณาธิการ. ยาต้านจุลชีพที่สำคัญ 2. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1. กรุงเทพฯ: ตรีเทพบุ๊คโปรเลส; 2558. หน้า 390-418.
Hamill RJ. Amphotericin B formulations: a comparative review of efficacy and toxicity. Drugs 2013;73(9):919-34. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0069-4. PMID: 23729001.
Fanos V, Cataldi L. Amphotericin B-induced nephrotoxicity: a review. J Chemother. 2000;12(6):463-70. doi: 10.1179/joc.2000.12.6.463. PMID: 11154026.
Zietse R, Zoutendijk R, Hoorn EJ. Fluid, electrolyte and acid–base disorders associated with antibiotic therapy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2009;5(4):193-202. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2009.17. PMID: 19322184.
Patterson RM, Ackerman GL. Renal tubular acidosis due to amphotericin B nephrotoxicity. Arch Intern Med. 1971;127(2):241-4. doi:10.1001/archinte.1971.00310140069007.
Zager RA, Bredl CR, Schimpf BA. Direct amphotericin B-mediated tubular toxicity: assessments of selected cytoprotective agents. Kidney Int. 1992;41(6):1588-94. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.229. PMID: 1501413.
ศิริลักษณ์ อนันต์ณัฐศิริ. Amphotericin B: deoxycholate and lipid complex. ใน: ธนาสนธิ์ ธรรมกุลและคณะ, บรรณาธิการ. Synopsis in antimicrobial therapy. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1. กรุงเทพฯ: โฮลิสติก พับลิชชิ่ง; 2561. หน้า 532-40.
สายชล ชำปฏิ, สัณห์ อภัยสวัสดิ์, มนต์ชัย ศิริบำรุงวงศ์. การเปรียบเทียบความเป็นพิษต่อไตและภาวะระดับโพแทสเซียมในเลือดต่ำจากการบริหารยาแอมโฟเทอริซิน บี แบบวันเว้นวัน กับแบบทุกวัน ในผู้ป่วยโรคเยื่อสมองอักเสบคริปโตคอคคัส. วารสารไทยเภสัชศาสตร์และวิทยาการสุขภาพ. 2551;3(1):12-8.
Rocha PN, Kobayashi CD, de Carvalho AL, Dos Reis CD, Santos BM, Glesby MJ. Incidence, predictors, and impact on hospital mortality of amphotericin B nephrotoxicity defined using newer acute kidney injury diagnostic criteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(8):4759-69. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00525-15. PMID: 26014956.
Molloy SF, Kanyama C, Heyderman RS, Loyse A, Kouanfack C, Chanda D, et al. Antifungal combinations for treatment of cryptococcal meningitis in Africa. NEJM. 2018;378(11):1004-17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1710922. PMID: 29539274.
Meiring S, Fortuin-de SM, Kularatne R, Dawood H, Govender NP, GERMS-SA. Prevalence and hospital management of amphotericin B deoxycholate-related toxicities during treatment of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis in South Africa. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10(7):e0004865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004865. PMID: 27467556.
Bicanic T, Bottomley C, Loyse A, Brouwer AE, Muzoora C, Taseera K, et al. Toxicity of amphotericin B deoxycholate-based induction therapy in patients with HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(12):7224-31. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01698-15. PMID: 26349818.
Chisholm-Burns MA, Schwinghammer TL, Malone PM, Kolesar JM, Lee KC, Bookstaver PB. Pharmacotherapy principles and practice. 5th ed. McGraw-Hills; 2019.
ศิริรัตน์ อนุตระกูลชัย. Disorder of potassium balance: hypokalemia and hyperkalemia. ใน: พงศธร คชเสนีและคณะ, บรรณาธิการ. Fluid, electrolyte and acid-based disorders. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 2. กรุงเทพฯ: เท็กซ์ แอนด์ เจอร์นัล พับลิเคชั่น; 2560. 69-110.
Bahr NC, Rolfes MA, Musubire A, Nabeta H, Williams DA, Rhein J, et al. Standardized electrolyte supplementation and fluid management improves survival during amphotericin therapy for cryptococcal meningitis in resource-limited settings. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2014;25;1(2):ofu070. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofu070. PMID: 25734140.
World Health Organization. Guidelines on the diagnosis, prevention and management of cryptococcal disease in HIV-infected adults, adolescents and children: supplement to the 2016 consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
วิธีการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
บท
การอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2021 กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกอย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และบุคลากรในกองฯ หรือ ชมรมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ



