การพัฒนาระบบการให้คะแนนปัจจัยเสี่ยงสำหรับการคาดการณ์การเสียชีวิตในผู้ป่วยติดเชื้อ Acinetobacter baumannii ดื้อยาหลายขนาน โรงพยาบาลแพร่
คำสำคัญ:
Acinetobacter baumannii ที่ดื้อยาหลายขนาน, การเสียชีวิต, ปัจจัยเสี่ยง, ระบบการให้คะแนนบทคัดย่อ
ความเป็นมา: ปัจจุบันการติดเชื้อ Acinetobacter baumannii ดื้อยาหลายขนานเป็นปัญหาที่รุนแรงระดับโลก ในปัจจุบันยังไม่มีเครื่องมือเพื่อทำนายความเสี่ยงการเสียชีวิตที่สัมพันธ์กับการติดเชื้อ A. baumannii ดื้อยาหลายขนาน
วัตถุประสงค์: เพื่อพัฒนาระบบการให้คะแนนความเสี่ยงในการทํานายอัตราการเสียชีวิตในผู้ป่วยติดเชื้อ A. baumannii ดื้อยาหลายขนานที่เข้ารับการรักษาในหอผู้ป่วย ณ โรงพยาบาลแพร่ นำมาสู่การสร้างมาตรฐานการเฝ้าระวัง ควบคุม ป้องกัน ตรวจติดตาม และการดูแลรักษาผู้ป่วยอย่างใกล้ชิดและเหมาะสม
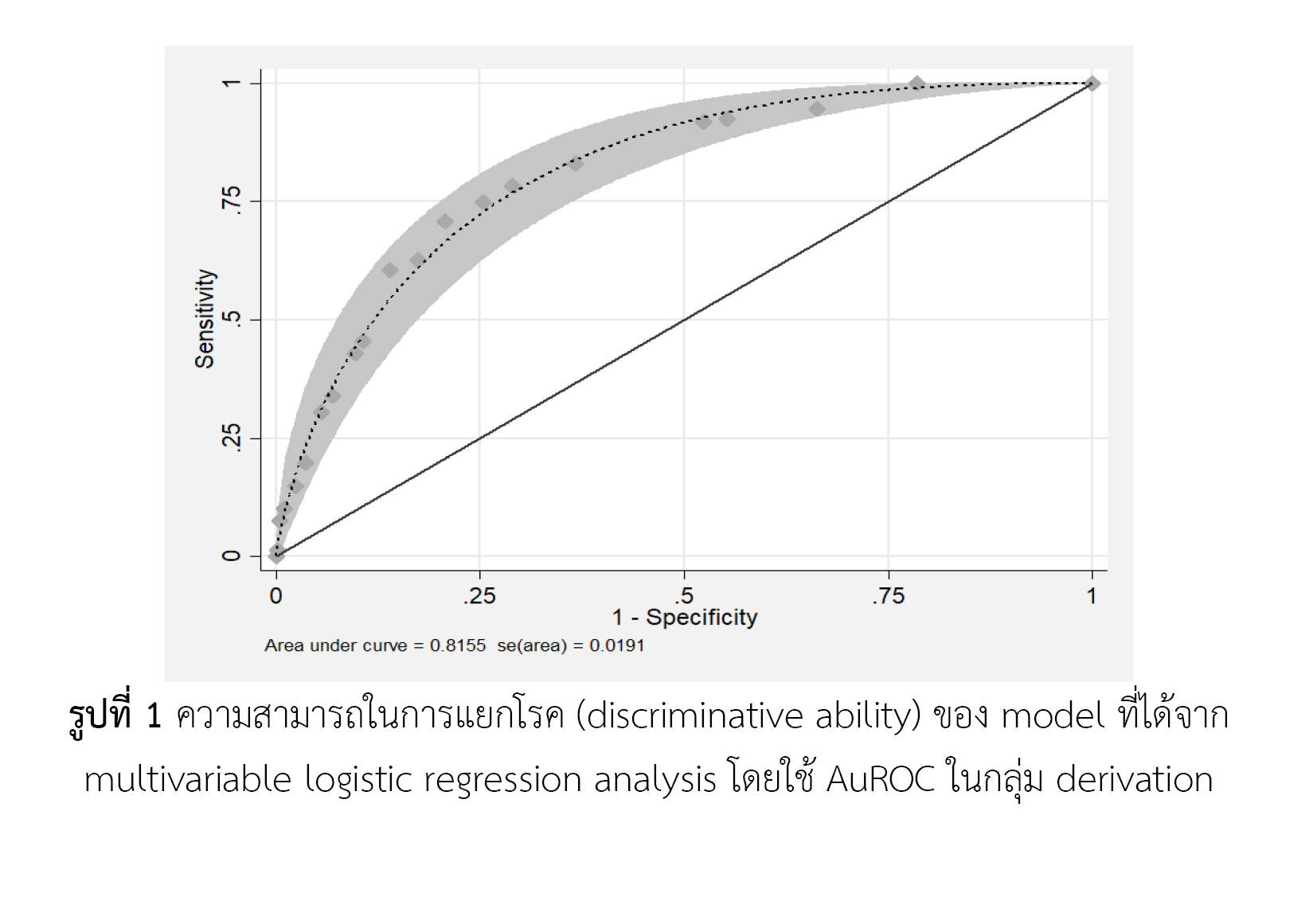
วิธีการศึกษา: การวิจัยครั้งนี้เป็นการเก็บรวบรวมข้อมูลย้อนหลัง (retrospective cohort study) จากเวชระเบียนผู้ป่วยที่เข้ารับการรักษาแบบผู้ป่วยในและจากฐานข้อมูลสารสนเทศทางเภสัชกรรม โรงพยาบาลแพร่ โดยเก็บรวบรวมข้อมูลผู้ป่วย ตั้งแต่วันที่ 1 ตุลาคม พ.ศ. 2560 ถึง 31 มีนาคม พ.ศ. 2564 วิเคราะห์หาปัจจัยที่สัมพันธ์กับการเสียชีวิต โดยวิธี univariate analysis และ multivariate analysis ด้วยวิธีการวิเคราะห์ตัวแปรแบบถดถอย และหาดัชนีทำนายความเสี่ยงต่อการเสียชีวิต โดยใช้ค่าสัมประสิทธิ์สหสัมพันธ์ วิเคราะห์ความสามารถในการทำนายการเสียชีวิตของเครื่องมือ โดยใช้ area under receiving operator curves (AuROC) และทดสอบ goodness-of-fit เครื่องมือจะถูกนำไปทดสอบความสามารถในการทำนายอัตราการเสียชีวิตในกลุ่มประชากรเพื่อทดสอบเครื่องมือ
ผลการศึกษา: ปัจจัยสำหรับใช้ในการพยากรณ์มี 6 ปัจจัยที่มีความสำคัญทางคลินิกและสามารถทำนายการเสียชีวิตได้อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ ได้แก่ 1. ผู้ป่วยที่มีภูมิคุ้มกันบกพร่อง 2. ภาวะปอดอุดกั้นเรื้อรัง 3. ผู้ที่เข้ารับการรักษาในแผนกผู้ป่วยหนัก 4. ใส่ท่อช่วยหายใจ 5. ภาวะช็อคจากการติดเชื้อ 6. ได้รับยาปฏิชีวนะภายใน 3 เดือนที่ผ่านมา จากการทดสอบความแม่นยำภายในพบว่า เครื่องมือมีความสามารถในการทำนายได้ดี (AuROC 76.21%) ความน่าจะเป็นเมื่อแบบทดสอบเป็นบวกของกลุ่มความเสี่ยงต่ำและความสูงของการเสียชีวิตมีค่าเท่ากับ 1.50 (95%CI: 1.27-1.77) และ 4.50 (95%CI: 2.65-7.66) ตามลำดับ
สรุปผล: เครื่องมือระบบการให้คะแนนความเสี่ยงในการทํานายอัตราการเสียชีวิตในผู้ป่วยติดเชื้อ A. baumannii ดื้อยาหลายขนาน อาจจะมีประโยชน์ต่อการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมร่วมกับทีมสหสาขาวิชาชีพในการดูแลผู้ป่วยติดเชื้อ A. baumannii ดื้อยาหลายขนาน อย่างไรก็ตามควรนำการศึกษานี้ไปทำการทดสอบความตรงภายนอกของเครื่องมือในกลุ่มประชากรอื่นๆ ก่อนนำไปใช้ในทางปฏิบัติ
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Anudit C, Kooltheat N, Potup P, Pankla Sranujit R, Usuwanthim K. Nosocomial infection of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Thailand. Am J Infect Control. 2016;44(10):1161-3.
Wong D, Nielsen TB, Bonomo RA, Pantapalangkoor P, Luna B, Spellberg B. Clinical and pathophysiological overview of Acinetobacter infections: A century of challenges. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2017 Jan;30(1):409-47.
Ilsan NA, Lee Y-J, Kuo S-C, Lee I-H, Huang T-W. Antimicrobial resistance mechanisms and virulence of colistin and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from a teaching hospital in Taiwan. Microorganisms. 2021;9(6):1295.
Wisplinghoff H, Bischoff T, Tallent SM, Seifert H, Wenzel RP, Edmond MB. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: Analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin Infect Dis an Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2004;39(3):309-17.
Alotaibi T, Abuhaimed A, Alshahrani M, Albdelhady A, Almubarak Y, Almasari O. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a critical care setting: A tertiary teaching hospital experience. SAGE open Med. 2021;9:20503121211001144. doi: 10.1177/20503121211001144.
Onraj W, Kridsada S. Epidemics of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Buengkan hospital, Thailand, 2016 -2019. Dep Heal Serv Support J [Internet]. 2022;18(1):31-8. Available from: https://hss.moph.go.th/fileupload_doc/2022-05-03-1-22-105432236.pdf
Sunenshine RH, Wright M-O, Maragakis LL, Harris AD, Song X, Hebden J, et al. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter infection mortality rate and length of hospitalization. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13(1):97-103.
Phumart P, Phodha T, Thamlikitkul V, Riewpaiboon A, Prakongsai P, Limwattananon S. Health and economic impacts of antimicrobial resistant infections in Thailand : A preliminary study. J Heal Syst Res [Internet]. 2012;6(3):352-60. Available from: https://kb.hsri.or.th/dspace/bitstream/handle/11228/3699/hsri-journal-v6n3-p352-360.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y
Zhou H, Yao Y, Zhu B, Ren D, Yang Q, Fu Y, et al. Risk factors for acquisition and mortality of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bacteremia: A retrospective study from a Chinese hospital. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(13):e14937. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014937.
Phodha T, Riewpaiboon A, Malathum K, Coyte PC. Annual relative increased in inpatient mortality from antimicrobial resistant nosocomial infections in Thailand. Epidemiol Infect. 2019;147:e133. doi: 10.1017/S0950268818003436.
Perez F, Hujer AM, Hujer KM, Decker BK, Rather PN, Bonomo RA. Global challenge of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob agents chemother. 2007;51(10):3471-84.
Manchanda V, Sanchaita S, Singh N. Multidrug resistant acinetobacter. J Glob Infect Dis. 2010;2(3):291-304. doi: 10.4103/0974-777X.68538.
Busani S, Serafini G, Mantovani E, Venturelli C, Giannella M, Viale P, et al. Mortality in patients with septic shock by multidrug resistant bacteria: Risk factors and Impact of sepsis treatments. J Intensive Care Med. 2019;34(1):48-54.
Jung JY, Park MS, Kim SE, Park BH, Son JY, Kim EY, et al. Risk factors for multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bacteremia in patients with colonization in the intensive care unit. BMC Infect Dis. 2010;10(1):228. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-228.
Tosi M, Erika R, Biasi S, Munari E, Venturelli S, Coloretti I, et al. Multidrug resistant bacteria in critically ill patients: A step further antibiotic therapy. J Emerg Crit Care Med. 2018;2:103-11. doi: 10.21037/jeccm.2018.11.08.
Roy S, Chowdhury G, Mukhopadhyay AK, Dutta S, Basu S. Convergence of biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Front Med. 2022;9:793615. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.793615.
Nseir S, Di Pompeo C, Cavestri B, Jozefowicz E, Nyunga M, Soubrier S, et al. Multiple-drug-resistant bacteria in patients with severe acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Prevalence, risk factors, and outcome. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(12):2959-66.
Chen G, Xu K, Sun F, Sun Y, Kong Z, Fang B. Risk factors of multidrug-resistant bacteria in lower respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2020;2020:7268519. doi: 10.1155/2020/7268519.
Gunalan A, Sarumathi D, Sastry AS, Ramanathan V, Rajaa S, Sistla S. Effect of combined colistin and meropenem against meropenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa by checkerboard method: A cross sectional analytical study. Indian J Pharmacol. 2021;53(3):207-12.
Saelim W, Changpradub D, Thunyaharn S, Juntanawiwat P, Nulsopapon P, Santimaleeworagun W. Colistin plus sulbactam or fosfomycin against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Improved efficacy or decreased risk of nephrotoxicity? Infect Chemother. 2021;53(1):128-40.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
วิธีการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
บท
การอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2022 กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกอย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และบุคลากรในกองฯ หรือ ชมรมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ



