The Effect of Telepharmacy on Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus in Srisangwan Hospital, Mae Hong Son Province
Keywords:
telepharmacy, type II diabetes mellitusAbstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is recognized as a significant public health problem worldwide. Advances in telecommunication technology have led to the development of telepharmacy services to monitor and resolve about drug-related problems in patients.
Objective: To study the effect of telepharmacy on clinical outcomes (HbA1C), knowledge of medication usage, medication adherence, and drug-related problems in patients with type II diabetes mellitus.
Methods: The study was a quasi-experimental research conducted with 45 patients with type II diabetes mellitus at Srisangwan Hospital, Mae Hong Son Province. Data collection was undertaken from July to December 2023. The study instruments included a questionnaire comprising data related to personal information, a knowledge test on the use of medication, a medication adherence assessment form, and a record of medical history and drug-related problems. Data analysis was performed using descriptive statistics and a paired sample t-test.
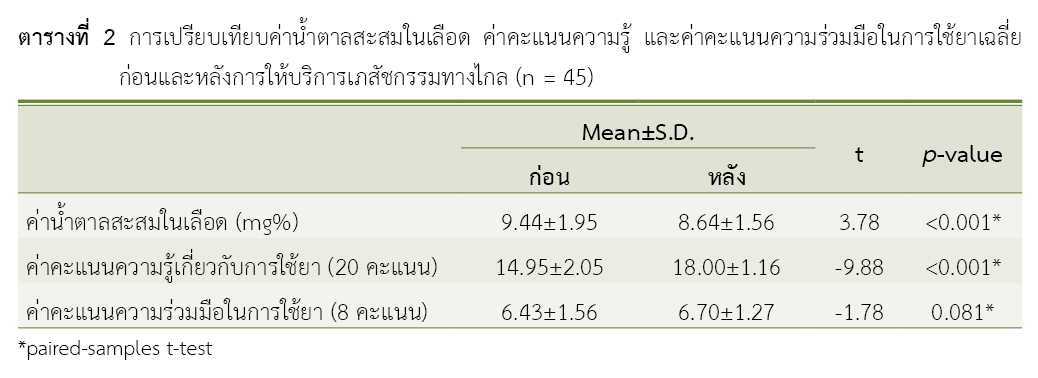
Results: The results before and after the delivery of telepharmacy revealed the following: The mean glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) levels were 9.44±1.95 and 8.64±1.56, indicating a statistically significant decrease (p-value<0.001). The mean scores for knowledge of medication (20 points) were 14.95±2.05 and 18.00±1.16, showing a statistically significant increase (p-value<0.001). The mean scores of medication adherence (8 points) were 6.43±1.56 and 6.70±1.27, demonstrating an increase, but with no significant difference. In terms of drug-related problems, the most common issues were related to the effectiveness of drug treatment (81.5%) and adverse drug reactions (16.7%). The causes of problems were as follows: 37.9% forgot to take medicine or stopped taking medicine or reduced the dosage on their own, 24.2% lacked dietary control, and 12.2% had inappropriate timing or dosing intervals.
Conclusion: The results of providing telepharmacy to patients with type II diabetes mellitus showed that patients' knowledge of medication usage increased, and drug-related problems were resolved, which resulted in a decrease in HbA1C levels. However, the HbA1C level did not reach the target level.
References
International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes around the world in 2021. [Internet]. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2021 [cited 2023 May 3]. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/
กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. กรมควบคุมโรค. จำนวนและอัตราตายด้วย 5 โรคไม่ติดต่อ (ปี2560-2564). [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: กรมควบคุมโรค กระทรวงสาธารณสุข; 2566 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566]. สืบค้นจาก: https://www.ddc.moph.go.th/dncd/forecast_detail.php?publish=13744
กรมควบคุมโรค. สำนักสื่อสารและพัฒนาพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ. รณรงค์วันเบาหวานโลก 2566 มุ่งเน้นให้ความรู้ประชาชนถึงความเสี่ยงโรคเบาหวานและหากตรวจพบก่อนจะลดภาวะแทรกซ้อนที่รุนแรงได้ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: กรมควบคุมโรค; 2566 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 14 พ.ย. 2566]. สืบค้นจาก: https://ddc.moph.go.th/brc/news.php?news=38403&deptcode=brc
โรงพยาบาลศรีสังวาลย์. กลุ่มงานเวชกรรมสังคม. ข้อมูลผู้ป่วยโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้องรัง ปีงบประมาณ 2564-2565. แม่ฮ่องสอน: โรงพยาบาลศรีสังวาลย์; 2565.
โรงพยาบาลศรีสังวาลย์. กลุ่มงานเภสัชกรรม. รายงานบริหารเวชภัณฑ์ ปีงบประมาณ 2564-2565. แม่ฮ่องสอน: โรงพยาบาลศรีสังวาลย์; 2565.
วนิดา พงษ์ศักดิ์ชาติ. การคำนวณหาขนาดตัวอย่างเพื่องานวิจัย. ชลบุรี: มหาวิทยาลัยบูรพา; 2563 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566]. สืบค้นจาก: https://thaimed.buu.ac.th/public/backend/upload/thaimed.buu.ac.th/document/file/document161717461088510200.pdf
ปริตตา ไชยมล, สงวน ลือเกียรติบัณฑิต, วรนุช แสงเจริญ. ผลของการให้ความรู้โดยเภสัชกรร่วมกับการใช้ภาพถ่ายแสดงวิธีการใช้ยาสำหรับผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวาน. วารสารเภสัชกรรมไทย [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2560 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566];9(2):475-88. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/TJPP/article/view/170882/122810
Morisky DE, Ang F, Krousel-Wood M, Ward HJ. Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting. J Clin Hypertens. 2008;10(5):348-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.07572.x.
Sakthong P, Chabunthom R, Charoenvisuthiwong R. Psychometric properties of the Thai version of the 8-item morisky medication adherence scale in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43(5):950-7. doi: 10.1345/aph.1l453.
รจเรศ หาญรินทร์. การจัดประเภทของปัญหาเกี่ยวกับยา. วารสารเภสัชกรรมไทย [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2552 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566];1:84-96. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/TJPP/article/view/168324/121118
Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe Association. PCNE classification for drug-related problems V9.1 [Internet]. Zuidlaren: Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe Association; 2020 [cited 2023 May 15]. Available from: https://www.pcne.org/upload/files/417_PCNE_classification_V9-1_final.pdf
สภาเภสัชกรรม. ศูนย์การศึกษาต่อเนื่อง. การอบรมระยะสั้น หลักสูตรประกาศนียบัตรการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรม (สาขาการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมผู้ป่วยนอก) รุ่นที่ 8 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: สภาเภสัชกรรม; 2560 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 15 พ.ค. 2566]. สืบค้นจาก: https://ccpe.pharmacycouncil.org/index.php?option=seminar_detail&subpage=seminar_detail&id=1261
สภาเภสัชกรรม. ประกาศสภาเภสัชกรรม ที่ 62/2565 เรื่อง แนวทางเกี่ยวกับมาตรฐานการให้บริการเภสัชกรรมทางไกล (Telepharmacy) ประกาศ ณ วันที่ 30 สิงหาคม พ.ศ. 2565 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: สภาเภสัชกรรม; 2565 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566]. สืบค้นจาก: https://www.pharmacycouncil.org/index.php?option=content_detail&menuid=68&itemid=2966&catid=0
อัญชนา พืดขุนทด. การบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ได้รับการรักษาด้วยยาฉีดอินซูลิน โรงพยาบาลบ้านด่าน. วารสารการแพทย์โรงพยาบาลศรีสะเกษ สุรินทร์ บุรีรัมย์ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2565 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566];38(1):237-46. สืบค้นจาก: https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/MJSSBH/article/view/262536/179189
Wang W, Geng L, Sun C, Li H, Wang J. Efficacy of pharmaceutical care in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension: a randommized controlled trial. Int J Clin Pract. 2022;2022:7681404. doi: 10.1155/2022/7681404.
ภาณุ วิริยานุทัย, กฤษฎิ์ ทองบรรจบ, ศรีประไพ อินทร์ชัยเทพ, วิชาดา มะลิ, ชนินาถ เครือนวล. ผลการบริบาลเภสัชกรรมโดยการออกเยี่ยมบ้านในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลได้. วารสารสาธารณสุขและสุขภาพศึกษา [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2565 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566];2(2):40-58. สืบค้นจาก: https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/tjphe/article/view/258865/176864
พุทธิดา โภคภิรมย์, กรกมล รุกขพันธ์. ผลของการสัมภาษณ์เพื่อเสริมสร้างแรงจูงใจแบบสั้นร่วมกับการให้ความรู้และการติดตามทางโทรศัพท์โดยเภสัชกร ในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2: การศึกษาเชิงทดลองแบบสุ่มและมีกลุ่มควบคุม. วารสารเภสัชกรรมไทย [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2562 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566];12(4):984-96. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/TJPP/article/view/190521
สุภาพร สนองเดช. ผลของการบริบาลเภสัชกรรมในผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานและโรคความดันโลหิตสูงในสถานบริการโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลเครือข่ายโรงพยาบาลเลย. เภสัชกรรมคลินิก [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2565 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566];28(3):85-97. สืบค้นจาก: https://thaidj.org/index.php/TJCP/article/view/12887/10823
สิรวิชญ์ พันธนา, ประภาเพ็ญ สุวรรณ, สุรี จันทรโมลี, สุธรรม นันทมงคลชัย. การพัฒนารูปแบบการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมสำหรับผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานโดยการมีส่วนร่วมของชุมชน อำเภอเมืองบึงกาฬ จังหวัดบึงกาฬ. วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2562 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 พ.ค. 2566];6(3):1-13. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/scnet/article/view/151582/142524
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Health Administration Division, Office of the Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Public Health and The Society of Hospital Pharmacist, Ministry of Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกอย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และบุคลากรในกองฯ หรือ ชมรมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ



