The Development of Analytical Method Validation of HPLC Method for Determination of Cannabidiol (CBD) in a 1% CBD Cream
Keywords:
cannabidiol (CBD), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), CBD cream, analytical method validationAbstract
Background: Chao Phya Abhaibhubejhr Hospital has developed a 1.0% w/w cannabidiol (CBD) cream formulation for use in patients with psoriasis and dermatitis. Therefore, developing an accurate and reliable analytical method for CBD quantification is essential for product quality control.
Objective: To develop and validate a quantitative analytical method for CBD in the 1.0% w/w CBD cream formulation using the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) technique.
Methods: The CBD in the cream formulation was analyzed using HPLC. The analysis utilized a NexLeaf CBX for Potency (C18) column maintained at 35°C, with a detection wavelength of 220 nm. A gradient elution of 0.085% orthophosphoric acid in deionized water and 0.085% orthophosphoric acid in acetonitrile was used as the mobile phase, at a flow rate of 1.6 mL/min. System suitability, specificity, linearity, range, accuracy, and precision were evaluated to validate the analytical method in accordance with ICH Q2(R1) guidelines.
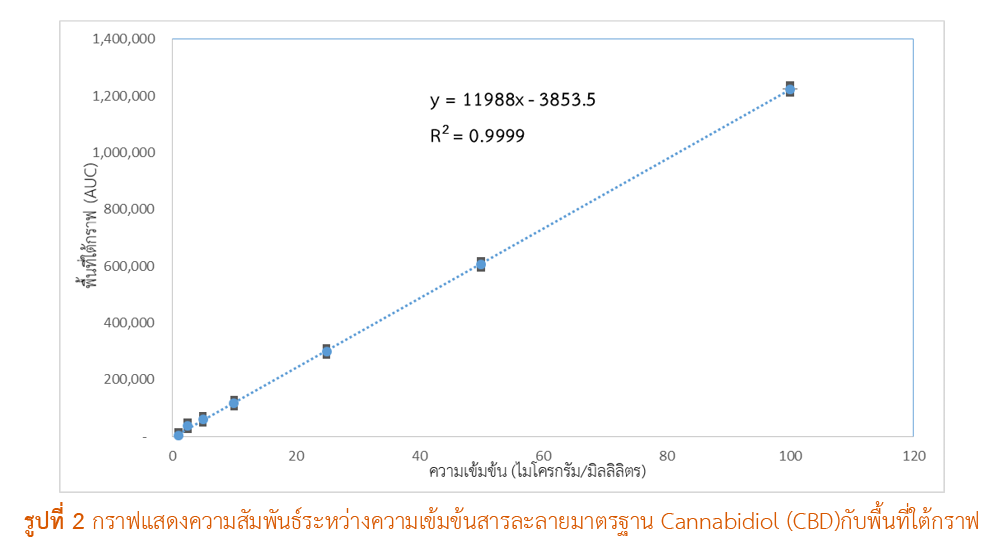
Results: The developed quantitative method demonstrated specificity in separating CBD without interference from the cream base. The method showed good linearity in the concentration range of 1–100 µg/mL (R² = 0.9999). The accuracy, reported as recovery percentage, ranged from 98.5% to 101.2%, and the precision, reported as the relative standard deviation (%RSD), was less than 1.0% for both intra-day and inter-day tests. When the validated method was applied to analyze two samples of the 1.0% CBD cream, the measured CBD concentrations were 1.1023% and 1.1918% w/w.
Conclusion: The developed HPLC method for the quantitative analysis of CBD in the 1.0% w/w cream formulation meets international standards for active pharmaceutical ingredient analysis in terms of accuracy, precision, and reliability. It is suitable for use in quality control of CBD cream products at the hospital level.
References
Martinez Naya N, Kelly J, Corna G, Golino M, Abbate A, Toldo S. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of action of cannabidiol. Molecules. 2023;28(16):5980. doi: 10.3390/molecules28165980.
Baswan SM, Klosner AE, Glynn K, Rajgopal A, Malik K, Yim S, Stern N. Therapeutic potential of cannabidiol (CBD) for skin health and disorders. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020;13:927-42. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S286411.
Puaratanaarunkon T, Sittisaksomjai S, Sivapornpan N, Pongcharoen P, Chakkavittumrong P, Ingkaninan K, et al. Topical cannabidiol-based treatment for psoriasis: a dual-centre randomized placebo-controlled study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(9):e718-20. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18215.
Sarma ND, Waye A, ElSohly MA, Brown PN, Elzinga S, Johnson HE, et al. Cannabis inflorescence for medical purposes: USP considerations for quality attributes. J Nat Prod. 2020;83(4):1334-51. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01200.
ธนวัฒน์ ทองจีน, สรเพชร มาสุด, พีรธรรม เทียมเทียบรัตน์, สายัณห์ เรืองเขตร, ศักดิ์วิชัย อ่อนทอง, พิเชฐ บัญญัติ, และคณะ. การพัฒนาวิธีวิเคราะห์ปริมาณแคนนาบินอยด์ในใบกัญชาด้วยวิธี ultra high performance liquid chromatography. วารสารกรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2564 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 20 ก.พ. 2568];63(3):505-23. สืบค้นจาก: https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/dmsc/article/view/252742
Wilson WB, Abdul-Rahman M. Determination of 11 cannabinoids in hemp plant and oils by liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. Chromatographia. 2022;85(1):115-25. doi: 10.1007/s10337-021-04114-y.
Mandrioli M, Tura M, Scotti S, Gallina Toschi T. Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis sativa L. Molecules. 2019;24(11):2113. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112113.
Schettino L, Prieto M, Benedé JL, Chisvert A, Salvador A. A rapid and sensitive method for the determination of cannabidiol in cosmetic products by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Cosmetics. 2021;8(2):30. doi: 10.3390/cosmetics8020030.
Galant N, Czarny J, Powierska-Czarny J, Piotrowska-Cyplik A. Development and validation of the LC–MS/MS method for determination of 130 natural and synthetic cannabinoids in cannabis oil. Molecules. 2022;27(23):8601. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238601.
กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์. สำนักยาและวัตถุเสพติด. Thai Herbal Pharmacopoeia 2021 Supplement 2024 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: สำนักยาและวัตถุเสพติด กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข; 2567 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 ก.พ. 2568]. สืบค้นจาก: https://website.bdn.go.th/th/e-book/detail/nGM4ZtWewEb3QWewEb3Q
United States Pharmacopeia. General Chapter, <621> Chromatography [Internet]. Rockville (MD): The United States Pharmacopeial Convention; 2025 [cited 2025 Feb 13]. Available from: https://doi.usp.org/USPNF/USPNF_M99380_09_01.html
The International Council for Harmonization of Technical Requirements of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Validation of analytical procedures - Scientific guideline Q2(R1) [Internet]. Amsterdam: European Medicines Agency; 1995 [cited 2025 Jan 21]. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-guideline-q2r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology-step-5-first-version_en.pdf
นพวัฒน์ เพ็งคำศรี. การตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของวิธีวิเคราะห์ทางเภสัชกรรม [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: ศูนย์การศึกษาต่อเนื่องทางเภสัชศาสตร์ สภาเภสัชกรรม; 2560 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 ม.ค. 2567]. สืบค้นจาก: https://ccpe.pharmacycouncil.org/index.php?option=article_detail&subpage=article_detail&id=338
AOAC. Appendix F: Guidelines for standard method performance requirements [Internet]. Rockville (MD): AOAC International; 2016 [cited 2025 Mar 11]. Available from: https://www.aoac.org/resources/guidelines-for-standard-method-performance-requirements/
Kühn-Hebecker A. New quality standards for medical cannabis and CBD [Internet]. Heidelberg: Concept Heidelberg GmbH; 2025 [cited 2025 Jun 1]. Available from: https://www.gmp-journal.com/current-articles/details/new-quality-standards-for-medical-cannabis-and-cbd.html
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Health Administration Division, Office of the Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Public Health and The Society of Hospital Pharmacist, Ministry of Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกอย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และบุคลากรในกองฯ หรือ ชมรมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ



