Risk Assessment of Patients with a History of Penicillin Allergy Using the PEN-FAST Tool for Drug Delabeling in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Keywords:
drug delabeling, history of penicillin allergyAbstract
Background: Patients with a documented penicillin allergy in hospital electronic medical records are labeled to prevent re-exposure; however, some may not be truly allergic. Evidence regarding the extent of false allergy labeling remains limited, even though such mislabeling can influence antibiotic prescribing practices and increase healthcare costs.
Objectives: To assess the prevalence and associated factors of patients with a recorded history of penicillin allergy who are suitable for referral to a drug delabeling process.
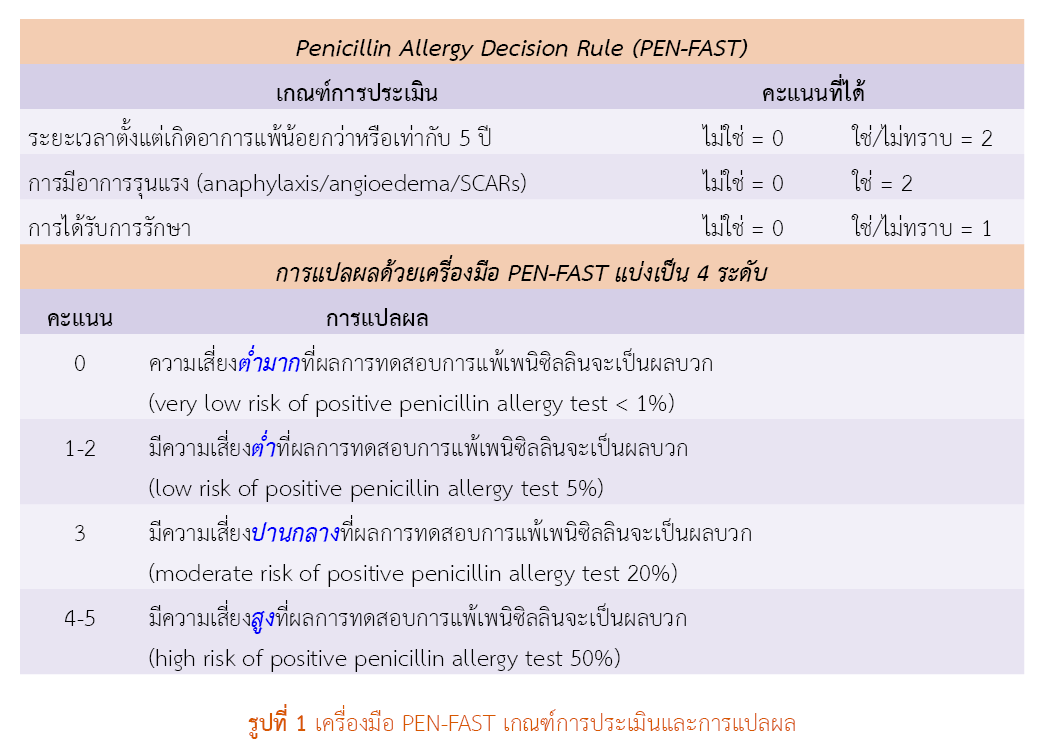
Methods: This retrospective analytical study included all patients with a recorded history of penicillin allergy in the hospital electronic medical record system between January 1, 2024, and December 31, 2024. Demographic data and allergy-related information were collected and evaluated using the PEN-FAST tool to determine patients’ risk levels for entering the drug delabeling process. The prevalence of low-risk patients unlikely to have a true allergy upon testing, as well as factors associated with the risk levels, were analyzed using logistic regression.
Results: Among 559 patients with a documented history of penicillin allergy, 123 (22.0%) had a PEN-FAST score < 3, indicating a low risk of a positive penicillin allergy test and suitability for drug delabeling. None of the demographic factors (gender, age) or clinical factors (allergy-related diseases, multiple drug allergies, patient-reported information, or documentation by healthcare personnel during allergic reactions) were significantly associated with the risk level for drug delabeling (p-value > 0.05).
Conclusion: According to the PEN-FAST assessment criteria, 22% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy were eligible to undergo an appropriate drug allergy testing. No factors demonstrated a statistically significant association (p-value > 0.05) with the risk level for proceeding with allergy de-labeling.
References
Blumenthal KG, Peter JG, Trubiano JA, Phillips EJ. Antibiotic allergy. Lancet. 2019;393(10167):183–98. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32218-9.
Macy E. Penicillin allergy: optimizing diagnostic protocols, public health implications, and future research needs. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;15(4):308-13. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000173.
Shenoy ES, Macy E, Rowe T, Blumenthal KG. Evaluation and management of penicillin allergy: a review. JAMA. 2019;321(2):188-99. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.19283.
Trubiano JA, Vogrin S, Chua KYL, Bourke J, Yun J, Douglas A, et al. Development and validation of a penicillin allergy clinical decision rule. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(5):745-52. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0403.
Alsulaiman JW, Kheirallah KA, Alrawashdeh A, Saleh T, Obeidat M, Alawneh YJ, et al. Risk Stratification of penicillin allergy labeled children: a cross-sectional study from Jordan. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2024;20:505-14. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S464511.
Mori F, Saretta F, Riscassi S, Caimmi S, Bottau P, Liotti L, et al. Risk factors for drug hypersensitivity reactions in children. Ital J Pediatr. 2024;50(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13052-024-01694-x.
Lee EY, Copaescu AM, Trubiano JA, Phillips EJ, Wolfson AR, Ramsey A. Drug allergy in women. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2023;11(12):3615-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2023.09.031.
Kvedariene V, Sitkauskiene B, Tamasauskiene L, Rudzeviciene O, Kasiulevicius V, Nekrosyte G, et al. Prevalence of self-reported drug hypersensitivity reactions among Lithuanian children and adults. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2019;47(1):32-7. doi: 10.1016/j.aller.2018.05.006.
Blumenthal KG, Li Y, Banerji A, Yun BJ, Long AA, Walensky RP. The cost of penicillin allergy evaluation. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6(3):1019-27.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.08.006.
Su C, Belmont A, Liao J, Kuster JK, Trubiano JA, Kwah JH. Evaluating the PEN-FAST clinical decision-making tool to enhance penicillin allergy delabeling. JAMA Intern Med. 2023;183(8):883-5. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.1572.
Palapinyo S, Klaewsongkram J, Mongkolpathumrat P, Leelakanok N, Yotsombut K. A multidisciplinary approach to verify and de-label of drug allergic histories in a university hospital in Thailand: a retrospective descriptive study. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2023;16(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40545-023-00513-8.
Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC. Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2018.
Camille EB, Lisa GW. Beta-lactam & other cell wall & membrane-active antibiotics. In: Katzung BG, Vanderah TW, editos. Basic and clinical pharmacology. 15th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2020. p.823–43.
Yohei D. Penicillins and β-lactamase inhibitors. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2020. p.251-67.e4
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Drug allergy: diagnosis and management [Internet]. n.p.: NICE; 2014 [cited 2025 Oct 3]. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg183/resources/drug-allergy-diagnosis-and-management-pdf-35109811020229
Anderson B, Gens K. PEN-FAST forward: accelerating penicillin allergy de-labeling [Internet]. Cranbury (NJ): Contagion Live; 2020 [cited 2025 Oct 1]. Available from: https://www.contagionlive.com/view/pen-fast-forward-accelerating-penicillin-allergy-de-labeling
Hanniet A, Puyraveau M, Castelain F, Pelletier F, Aubin F. Efficacy of the PEN-FAST score in a French cohort of patients with reported allergy to penicillins. Front Allergy. 2024;5:1439698. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2024.1439698.
Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters; American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Drug allergy: an updated practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;105(4):259–73. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2010.08.002.
Khan DA, Banerji A, Blumenthal KG, Phillips EJ, Solensky R, White AA, et al. Drug allergy: a 2022 practice parameter update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;150(6):1333-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.08.028.
Caubet JC, Kaiser L, Lemaître B, Fellay B, Gervaix A, Eigenmann PA. The role of penicillin in benign skin rashes in childhood: a prospective study based on drug rechallenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(1):218–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.08.025.
Pichichero ME, Pichichero DM. Diagnosis of penicillin, amoxicillin, and cephalosporin allergy: reliability of examination assessed by skin testing and oral challenge. J Pediatr. 1998;132(1):137-43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(98)70499-8.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Health Administration Division, Office of the Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Public Health and The Society of Hospital Pharmacist, Ministry of Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกอย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และบุคลากรในกองฯ หรือ ชมรมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ



