Incidence and Factors Associated with Renal Function Impairment in HIV-Infected Patients Receiving Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate+Lamivudine+Dolutegravir Drug Regimen at Trang Hospital
Keywords:
renal function impairment, TLD drug regimenAbstract
Background: HIV-infected patients receiving a tenofovir disoproxil fumarate + lamivudine + dolutegravir (TLD) drug regimen have an increased incidence of renal function impairment. There is no empirical evidence on the incidence and associated factors.
Objective: To study the incidence and factors associated with renal function impairment in HIV-infected patients receiving the TLD drug regimen.
Method: A retrospective cohort study of HIV-infected patients receiving the TLD drug regimen at the HIV Clinic, Trang Hospital, was conducted from February 2022 to March 2024. Renal function impairment was defined as a > 25% decrease from the baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Factors affecting the occurrence of renal function impairment were analyzed using logistic regression analysis.
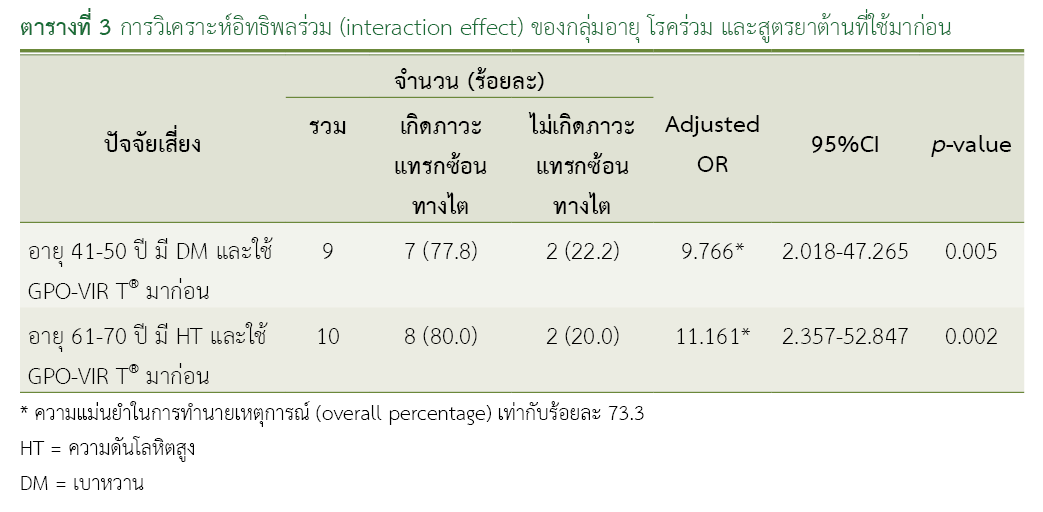
Results: A total of 1,402 HIV-infected patients were enrolled in the study, with an average age of 45.57 ± 10.44 years. After using TLD, 398 patients (28.4%) experienced renal function impairment. Factors associated with renal function impairment included age, comorbidities, and previous drug regimens. An interaction effect analysis found that patients aged 61-70 years with pre-existing hypertension and a history of using the GPO-VIR T® drug regimen had an adjusted odds ratio of 11.16 (95%CI: 2.36-52.85, p-value=0.002). Similarly, patients aged 41–50 years with pre-existing diabetes mellitus had an adjusted odds ratio of 9.77 (95%CI: 2.02-47.28, p-value=0.005).
Conclusion: Factors associated with renal function impairment include patients aged 61-70 years with pre-existing hypertension and a history of using the GPO-VIR T® drug regimen, as well as patients aged 41-50 years with pre-existing diabetes mellitus and a history of using GPO-VIR T®. Therefore, close monitoring of renal function should be carried out.
References
UNAIDS. UNAIDS Data 2024 [Internet]. Geneva: The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS); 2024 [cited 2024 Nov 30]. Available from: https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/data-book-2024_en.pdf
กรมควบคุมโรค. กองโรคเอดส์และโรคติดต่อทางเพศสัมพันธ์. สรุปสถานการณ์ผู้ป่วยเอดส์และการติดเชื้อเอชไอวีประเทศไทย 2567 [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: กรมควบคุมโรค; 2567 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 7 ม.ค. 2568]: สืบค้นจาก: https://hivhub.ddc.moph.go.th/executive/aids.php
เสาวนีย์ วิบุลสันติ, ศศิโสภิณ เกียรติบูรณกุล, โอภาส พุทธเจริญ, เอกจิตรา สุขกุล, รังสิมา โล่ห์เลขา. แนวทางการตรวจรักษาและป้องกันการติดเชื้อเอชไอวี ประเทศไทย ปี 2564/2565 [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: กองโรคเอดส์และโรคติดต่อทางเพศสัมพันธ์ กรมควบคุมโรค; 2565 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 7 ธ.ค. 2567]. สืบค้นจาก: https://ddc.moph.go.th/uploads/publish/1281020220531045539.pdf
Neuhaus J, Angus B, Kowalska JD, La Rosa A, Sampson J, Wentworth D, et al. Risk of all-cause mortality associated with nonfatal AIDS and serious non-AIDS events among adults infected with HIV. AIDS. 2010;24(5):697-706. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283365356.
Pettit AC, Giganti MJ, Ingle SM, May MT, Shepherd BE, Gill MJ, et al. Increased non-AIDS mortality among persons with AIDS-defining events after antiretroviral therapy initiation. J Int AIDS Soc. 2018;21(1):e25031. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25031.
Kolakowska A, Maresca AF, Collins IJ, Cailhol J. Update on adverse effects of HIV integrase inhibitors. Curr Treat Options Infect Dis. 2019;11(4):372-87. doi: 10.1007/s40506-019-00203-7.
วิศิษฏ์ ตันหยง, พีรยศ ภมรศิลปะธรรม, ฉัตรชัย ฉิ่นไพศาล. ทีโนโฟเวียร์และพิษต่อไตระดับเซลล์. วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์บูรพา [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2560 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 ม.ค. 2568];22(2):248-59. สืบค้นจาก: https://journal.lib.buu.ac.th/index.php/science/article/view/5183
Stellbrink HJ, Reynes J, Lazzarin A, Voronin E, Pulido F, Felizarta F, et al. Dolutegravir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1: 96-week results from a randomized dose-ranging study. AIDS. 2013; 27(11):1771-8. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283612419.
Koteff J, Borland J, Chen S, Song I, Peppercorn A, Koshiba T, et al. A Phase 1 study to evaluate the effect of dolutegravir on renal function via measurement of iohexol and para-aminohippurate clearance in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;75(4):990-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04440.x.
สโรชา งานวิวัฒน์ถาวร. การศึกษาปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการทำงานของไตผิดปกติในผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับยาต้านแบบรวมเม็ด (TLD) ในคลินิก ARV โรงพยาบาลถลาง จังหวัดภูเก็ต. วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยีนอร์ทเทิร์น [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2567 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 ม.ค. 2568];5(2):129-41. สืบค้นจาก: https://he03.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/scintc/article/view/2770
The Nephrology Society of Thailand. Clinical practice recommendation for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease in adults 2015. Bangkok: The Nephrology Society of Thailand; 2015.
Yan D, Wang Z, Wang Y, He S, Zheng Y, Yang X, et al. Performance of creatinine- and cystatin C-based equations for glomerular filtration rate estimation in HIV-1-infected individuals receiving dolutegravir+tenofovir disoproxil fumarate+lamivudine as initial antiretroviral therapy: a retrospective observational study. J Acquir Immnune Defic Syndr. 2022;91(S1):S35-41. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003044.
Lu L, Li X, Liu X, Han Y, Qiu Z, Song X, et al. Comparison of renal function biomarkers of serum creatinine and cystatin C in HIV-infected people on dolutegravir-containing therapy. Infect Drug Resist. 2022;15:1695-706. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S347054.
สุริยา แก้วภูมิแห่, จิรนันท์ โชติธรรมนาวี. ปัจจัยที่สัมพันธ์ต่อการบาดเจ็บที่ไตในผู้ติดเชื้อเอชไอวีที่ได้รับยาต้านเอชไอวีสูตรต่าง ๆ. วารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิก [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2567 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 ม.ค. 2568];30(3):181-91. สืบค้นจาก: https://thaidj.org/index.php/TJCP/article/view/15070
เชิดชัย สุนทรภาส, ภิรุญ มุตสิกพันธุ์, รัชฎาพร สุนทรภาส. ปัจจัยเสี่ยงของความเป็นพิษต่อไตในผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับยาทีโนโฟเวียร์ไดโซพรอกวิลฟูมาเรท ณ โรงพยาบาลตติยภูมิขั้นสูง. วารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2566 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 ม.ค. 2568];33(2):102-11. สืบค้นจาก: https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/TJHP/article/view/261514
ปอแก้ว เพ็ชรคำ, ระพีพงศ์ สุพรรณไชยมาตย์. อุบัติการณ์และปัจจัยเสี่ยงของการเกิดภาวะแทรกซ้อนทางไตจากการได้รับยา Tenofovir ของผู้ติดเชื้อเอชไอวี. วารสารวิชาการสาธารณสุข [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2559 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 ม.ค. 2568];25(1):92-103. สืบค้นจาก: https://thaidj.org/index.php/JHS/article/view/229
ดวงรัตน์ สุวรรณ, อัครวัฒน์ กรจิระเกษมศานติ์. อุบัติการณ์และปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการเกิดภาวะแทรกซ้อนทางไตในผู้ติดเชื้อเอชไอวีที่ได้รับการรักษาด้วยยา Tenofovir ในโรงพยาบาลนครพิงค์. วารสารโรงพยาบาลนครพิงค์ [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2563 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 ม.ค. 2568];11(2):173-85. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/jnkp/article/view/245652
Quinn KJ, Emerson CR, Dinsmore WW, Donnelly CM. Incidence of proximal renal tubular dysfunction in patients on tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Int J STD AIDS. 2010;21:(2)150-1. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2009.009464.
Lindeman TA, Duggan JM, Sahloff EG. Evaluation of serum creatinine changes with integrase inhibitor use in human immunodeficiency virus-1 infected adults. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3(2):ofw053. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofw053.
Doshi S, Ucanda M, Hart R, Hou Q, Terzian AS. Incidence and risk factors for renal disease in an outpatient cohort of HIV-Infected patients on antiretroviral therapy. Kidney Int Rep. 2019;4(8):1075-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2019.04.024.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Health Administration Division, Office of the Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Public Health and The Society of Hospital Pharmacist, Ministry of Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกอย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และบุคลากรในกองฯ หรือ ชมรมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ



