FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH BREAKFAST CONSUMPTION BEHAVIOR AMONG HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS AT SRISONGKHRAM WITTAYA SCHOOL, LOEI PROVINCE
Keywords:
Breakfast consumption behavior, Influencing factors, High school students, Adolescent nutritionAbstract
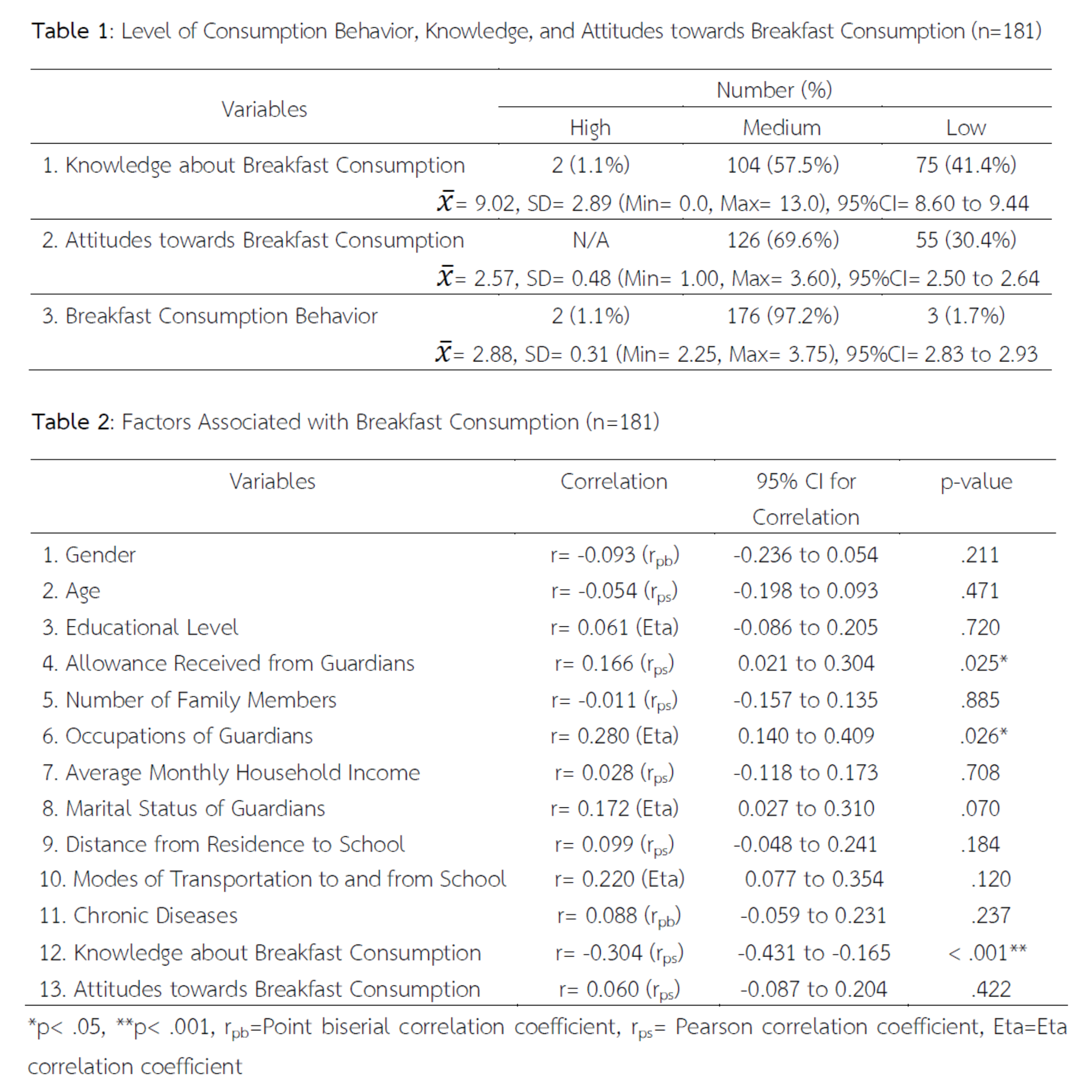
Breakfast is considered the most important meal of the day, as the body requires nutrients and energy to support its organs and brain function. Skipping breakfast can lead to insufficient nutrient and energy intake, resulting in fatigue, reduced physical activity, and lack of concentration in class. This cross-sectional analytical study aimed to examine factors associated with breakfast consumption behavior among high school students at Srisongkhram Wittaya School in Loei Province. The sample consisted of 181 students, selected through simple random sampling. Data were collected using a questionnaire with an Index of Item-Objective Congruence (IOC) between 0.67 and 1.00 and a reliability coefficient of 0.85. Descriptive statistics, including percentages, means, and standard deviations, were used for data analysis, along with inferential statistics such as point-biserial, eta, and Pearson’s correlation coefficients. The findings revealed that the majority of students had a moderate level of knowledge regarding breakfast consumption (57.5%, Mean = 9.02, SD = 2.89), a moderate level of attitude (69.6%, Mean = 2.57, SD = 0.48), and a moderate level of breakfast consumption behavior (97.2%, Mean = 2.88, SD = 0.31). Factors significantly associated with breakfast consumption behavior included parental income (r = 0.166, p = .025), parental occupation (r = 0.280, p = .026), age-appropriate weight (r = 0.424, p = .024), and knowledge of breakfast consumption (r = -0.304, p < .001). In conclusion, parental income, parental occupation, and age-appropriate weight showed a positive relationship with breakfast consumption behavior, while knowledge about breakfast consumption showed a negative correlation. It is recommended that nutrition education be promoted alongside positive attitude formation and support for school breakfast programs to enhance students' overall health and well-being.
References
Best J.W. & Kahn J.V. (2006). Research in education (10th ed.). Pearson Education Inc.
Bloom B.S. et al. (1971). Handbook on formative and summative evaluation of student learning. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Chaimongkol L. et al. (2021). Breakfast skipping in school children: A case study of schools in municipality and non-municipality area of Muang, Pattani Province. Journal of Nutrition Association of Thailand, 56(2), 36–49.
Chaiwut Y. et al. (2021). Factors associated with junk food consumption among Department of Community Health students in University in the Northern. UBRU Journal for Public Health Research, 10(2), 15-25.
Daniel, W.W. (2013). Biostatistics: A Foundation for Analysis in the Health Sciences. John Wiley & Sons.
Deejuthamanee R. et al. (2022). Breakfast consumption behavior among secondary school students in Bangkok. Thai Journal of Public Health, 52(1), 30–43.
Department of Health, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand. (2019). Breakfast is an important meal and shouldn't be overlooked. https://multimedia.anamai.moph.go.th/help-knowledgs/breakfast/
Liu Y. et al. (2021). Relationship between nutritional status and breakfast behaviors of rural primary and middle school students in a minority area of a city in Guizhou Province in 2019. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu, 50(4), 552–557.
Maumeng N. & Yoncharoenlump P. (2017). Nutritional status and dietary behavior of school children in diamond level health promotion school, Regional Health Promotion Center 2 Phitsanulok. Lanna Journal of Health Promotion & Environmental Health, 7(1), 67–74.
Mungvongsa A. & Khangwa K. (2020). Factors Related to Food consumption behavior of senior high school students in Watjuntrawart (Sukprasarnrat) School, Phetchaburi Province. Hua Hin Medical Journal, 5(1), 1-17.
Nithitantiwat P. & Udomsapaya W. (2017). Food Consumption Behavior among Thai Adolescents, Impacts, and Solutions. Journal of Phrapokklao Nursing College, Chanthaburi, 28(1), 122-128.
Panchaiyapum N. & Uttamavatin P. (2021). Food preference behaviors of high school students at Waengnoi Suksa School, Khon Kaen Province. KKU Journal for Public Health Research, 14(1), 49–56.
Rattanayoung T. et al. (2019). Consumption behaviors, overweight, and obesity among senior high school students in Nakhon Pathom Province. Journal of Nursing, Public Health, and Education, 20(3), 132–143.
Ruangying J. et al. (2016). Food consumption behavior of adolescents in Songkhla Province: Synthesis of literacy and factors influencing food consumption behavior. Journal of Liberal Arts, Prince of Songkla University, 8(1), 245–264.
Srisongkram Wittaya School, Thailand. (2020). Self-assessment report of the educational institution for the academic year 2020. http://www.srisongkram.ac.th
Sukrod, S. (2015). A study of the relation between food consumption, exercise habits, and obesity of students from Srinakharinwirot University Prasarnmit Demonstration School (Secondary). Srinakharinwirot Research and Development (Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences), 7(13), 200–210.
Suwan K. et al. (2021). Factors associated with Food Consumption Behaviors in Overweight Secondary School Students in Mueang District, Yala Province. Lanna Public Health Journal, 17(1), 40-51
Tritipsombut J. et al. (2020). Relationships between knowledge, attitude, and dietary behavior among the overweight and obese students in Elementary School. Journal of the Office DPC 7 Khon Kaen, 27(2), 92–100.
Wanprayoon R. et al. (2023). Factors Related to Breakfast Consumption Behavior of High school Student in the Lower Northern Region. Journal of Science and Technology Northern, 4(2), 13-28.
Wongwiriya S. et al. (2019). Factors associated with food consumption behaviors among high school students in Namdibwittayakom School, Pasang District, Lamphun Province. Journal of Public Health and Health Sciences Research, 1(2), 45–54
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Primary Health Care Journal (Northeastern Edition)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



