EFFECTS OF CONTROLLING HYPERTENSION PROGRAMS ACCORDING TO HEALTH BELIEFS CONCEPT AFFECTING CONTROLLING HYPERTENSION BEHAVIORS OF THE PATIENTS AT HEALTH PROMOTING HOSPITAL IN PLUAKDAENG DISTRICT RAYONG PROVINCE
Keywords:
Self-care behaviors, Behavioral modification program, Blood pressure control, Health promotionAbstract
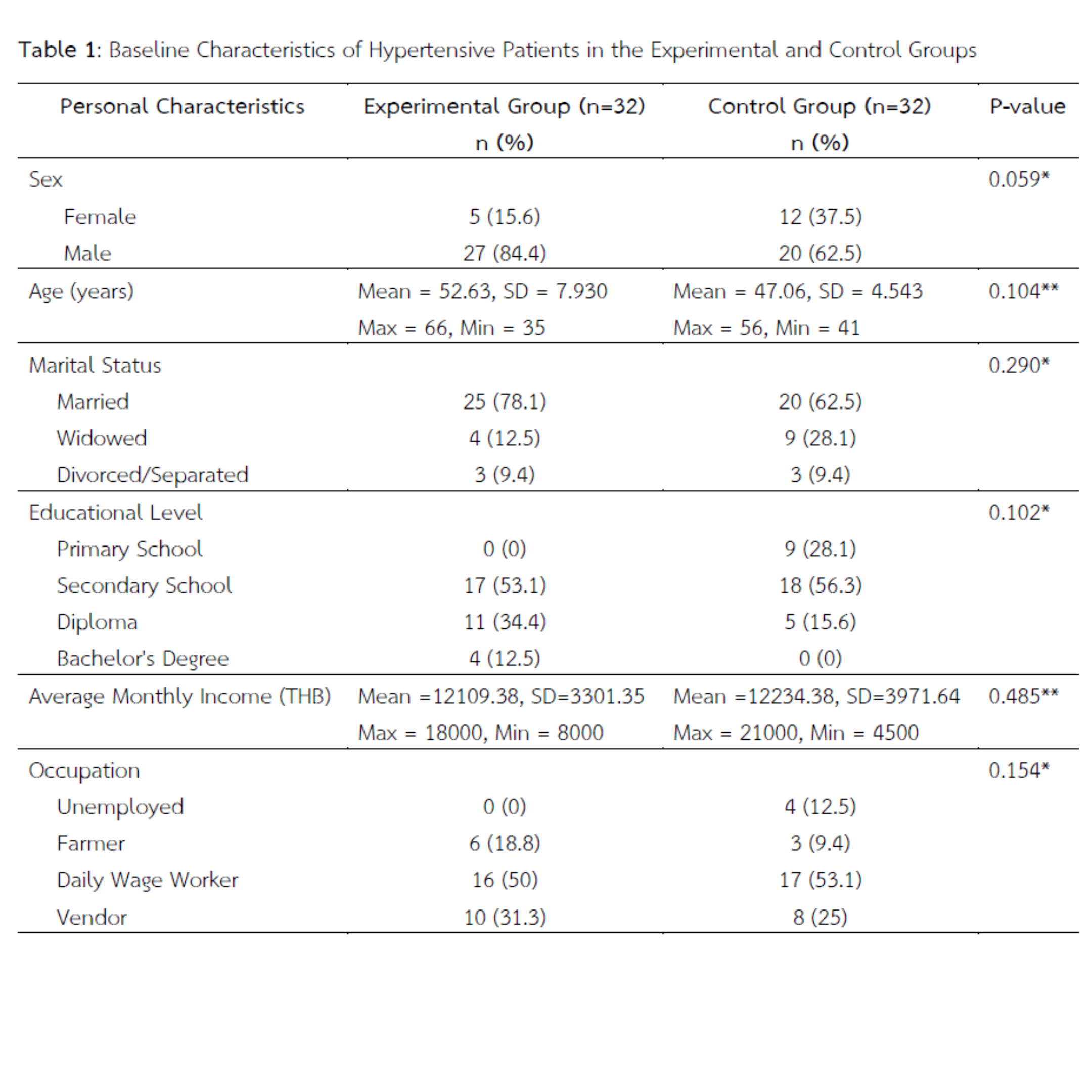
Hypertension is a major public health concern worldwide, including in Thailand. Without proper treatment and lifestyle modification, individuals with hypertension face a twofold increased risk of myocardial infarction and a fourfold increased risk of stroke. This quasi-experimental study aimed to examine the effects of a hypertension control program, based on the Health Belief Model, on self-care behaviors among hypertensive patients in a sub-district health-promoting hospital in Pluak Daeng District, Rayong Province. The sample consisted of 64 hypertensive patients, divided into an experimental group (n = 32) and a control group (n = 32). The experimental group received the hypertension control program over a six-week period. Data were collected using questionnaires and analyzed with descriptive statistics and inferential statistics, including paired samples t-test, independent samples t-test, and repeated measures ANOVA. The results revealed that, after the intervention, the experimental group showed a statistically significant improvement in overall self-care behavior scores compared to both baseline and the control group (p < 0.001). Regarding blood pressure control, the experimental group demonstrated a significant reduction in mean blood pressure from 146.19/93.56 mmHg before the intervention to 130.22/79.53 mmHg after the intervention, and further to 129.53/77.94 mmHg during follow-up (p < 0.001). The findings indicate that the behavioral modification program was effective in promoting appropriate health behaviors and in reducing blood pressure among hypertensive patients.
References
Anchalee, K. A. (2017). The Effect of a Motivational Program Combined with Exercise on Blood Pressure Among Individuals at Risk of Hypertension, [Thesis of Master of Nursing Science]. Graduate School: Chulalongkorn University.
Boonkam, A. (2022). Effectiveness of a Behavior Modification Program on Dietary Behavior Among High-Risk Group for Hypertension in Fak Tha Subdistrict, Fak Tha District, Uttaradit Province, [Thesis of Master of Public Health]. Graduate School: Uttaradit Rajabhat University.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Department of Disease Control, Non-Communicable Diseases Division. (2019, February 1). Health risk communication and health behavior development bureau: Hypertension situation report. https://ddc.moph.go.th/uploads/publish/1035820201005073556.pdf
Health Data Center (HDC). (2020, May 10). Rayong Provincial Public Health Office, Health Region 6. Ministry of Public Health https://hdc.moph.go.th/ryg/public/standardredetail/28ee19915688d2b19f474506c7c31d67
Health Data Center (HDC). (2022, April 5). Rayong Provincial Public Health Office, Health Region 6. Ministry of Public Health. https://hdc.moph.go.th/ryg/public/standard-report-detail/b57439ff27302ade8c38d1dd189644a4
Mahidol University Channel. (2019, November 14). Hypertension: The gateway to serious diseases. Mahidol University. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMG7OM7ZcJY
Phusritet, W. (2021). The effect of a health behavior modification program on hypertension control among patients in Nain Subdistrict, Phichai District, Uttaradit Province, [Thesis of Master of Public Health]. Graduate School: Uttaradit Rajabhat University.
Rosenstock I. M. et al. (1988). Social Learning Theory and the Health Belief Model. Health Education Quarterly, 15(2), 175-183.
Sriratana V. et al. (2021). Factors Affecting Emotional Intelligence. Journal of Roi Kaensarn Academi, 6(10), 408-422.
Tepsuriyanont, S. (2017). Medication Adherence Behavior Among Adult Patients with Hypertension. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses, 18(3), 115-122.
% Organic Sound Channel. (2020, October 30). 10-minute meditation guide (helps calm the mind more easily). Practice daily for a better life-turn negativity into positivity. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=up_8I2bmEjs
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Primary Health Care Journal (Northeastern Edition)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



