Outcome of Renal Function-Monitoring Program in HIV-Patient Treated with Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (TDF) and Nephrotoxicity: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Keywords:
TDF, nephrotoxicity, renal function-monitoring program, DRPsAbstract
Background: Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) is the main antiretroviral drug used in HIV patients due to its efficacy and few side effects. However, several studies have reported TDF-associated nephrotoxicity. Providing appropriate monitoring and patient counseling may help prevent these complications.
Objectives: To study the incidence and related factors of TDF-induced nephrotoxicity and drug-related problems (DRPs) before and after implementing a renal function-monitoring program.
Methods: This quasi-experimental research compared the results before and after using the renal function-monitoring program (during 2020-2023). Data analysis presents the frequency, percentage, and comparative incidence of nephrotoxicity from TDF before and after the renal function-monitoring program, expressed as odds ratios (OR). Logistic regression was used to analyze factors associated with renal complications.
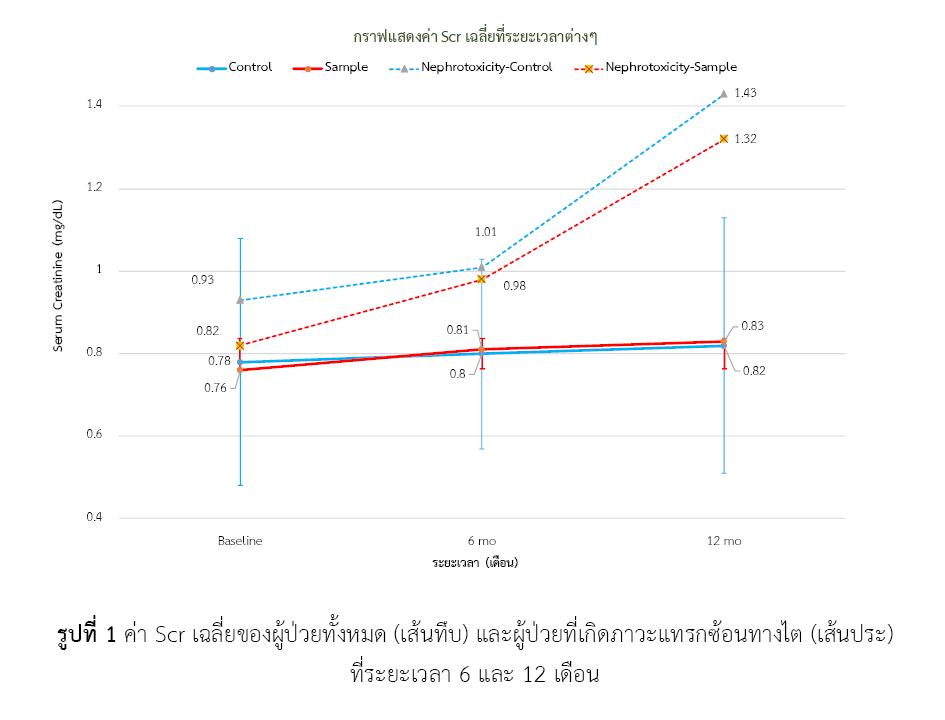
Results: A total of 607 patients participated (243 before implementation, 364 after implementation). Most patients were ≤50 years of age, used antiretroviral drugs (non-PI based regimen), and had used TDF for longer than 12 months. The group using the renal function-monitoring program had a lower incidence of nephrotoxicity (5.21% vs. 9.87%; OR 0.503; 95%CI: 0.269-0.939, p-value=0.031), reducing TDF-induced nephrotoxicity by 49.70%. There were fewer drug-related problems (DRPs) in this group (6.87% vs. 13.60%, p-value=0.009), and all DRPs were resolved by pharmacists. Correlated factors included male gender (OR 2.16; 95%CI: 1.05-4.46, p-value=0.037), use of protease inhibitors regimen (OR 3.63; 95%CI: 1.65-7.97, p-value=0.001), initial eGFR 60-90 ml/min/1.73m² (OR 3.89; 95%CI: 1.82-8.34, p-value<0.001), and the presence of drug-related problems (OR 5.39; 95%CI: 2.44-11.94, p-value<0.001).
Conclusion: A renal function-monitoring program implemented by pharmacists can help reduce TDF-induced nephrotoxicity. Pharmacist participation also reduces drug-related problems and prevents renal complications.
References
สุเมธ องค์วรรณดี, ศศิโสภิณ เกียรติบูรณกุล, อัญชลี อวิหิงสานนท์, เอกจิตรา สุขกุล, รังสิมา โล่เลขา. แนวทางการตรวจรักษาและป้องกันการติดเชื้อเอชไอวีประเทศไทย ปี 2560 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: สำนักโรคเอดส์ วัณโรค และโรคติดต่อทางเพศสัมพันธ์ กรมควบคุมโรค กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. 2560 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 1 ต.ค. 2563]. สืบค้นจาก: https://www.thaiaidssociety.org/thailand-hiv-aids-guideline/
สุนีย์ ชยางศุ. ผลของการทำงานของไตในผู้ป่วยเอดส์ที่ได้รับยาทีโนโฟเวียร์ติดตามเป็นเวลาสองปี. วารสารการแพทย์โรงพยาบาลศรีสะเกษ สุรินทร์ บุรีรัมย์ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2560 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 1 ต.ค.2563];32(1):1-11. สืบค้นจาก: https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/MJSSBH/article/view/118113
ปอแก้ว เพ็ชร์คํา, ระพีพงศ์ สุพรรณไชยมาตย์. อุบัติการณ์และปัจจัยเสี่ยงของการเกิดภาวะแทรกซ้อนทางไตจากการได้รับยา Tenofovir ของผู้ป่วยติดเชื้อเอชไอวี. วารสารวิชาการสาธารณสุข [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2559 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 1 ต.ค. 2563];25(1):92-103. สืบค้นจาก:https://thaidj.org/index.php/JHS/article/view/229/
วิบูลย์ อยู่ยงวัฒนา, ศิรานันต์ พลเหี้ยมหาญ, ประภาศรี อารยะพงศ์. การพัฒนาแนวปฏิบัติในการเฝ้าระวังการเกิดภาวะแทรกซ้อนทางไตจาก tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) ในผู้ป่วยติดเชื้อเอชไอวี โรงพยาบาลนครพนม. วารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิก [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2565 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 29 ก.พ.2567];28(1):1-14. สืบค้นจาก: https://thaidj.org/index.php/TJCP/article/view/12452
ดวงรัตน์ สุวรรณ, อัครวัฒน์ กรจิระเกษมศานติ์. อุบัติการณ์และปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการเกิดภาวะแทรกซ้อนทางไตในผู้ติดเชื้อเอชไอวีที่ได้รับการรักษาด้วยยา Tenofovir ในโรงพยาบาลนครพิงค์. วารสารโรงพยาบาลนครพิงค์ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2563 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 29 ก.พ.2567];11(2):173-85. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/jnkp/article/view/245652
กมลรัตน์ ณ หนองคาย. การบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมผู้ป่วยนอกที่ติดเชื้อเอชไอวีและผู้ป่วยเอดส์โรงพยาบาลศรีเชียงใหม่ จังหวัดหนองคาย. วารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิก [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2566 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 29 ก.พ. 2567];29(3):153-64. สืบค้นจาก:https://thaidj.org/index.php/TJCP/article/view/14144
ศศิธร แสงเนตร. ผลการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมในคลินิกผู้ป่วยติดเชื้อเอชไอวีและผู้ป่วยเอดส์ในโรงพยาบาลวาปีปทุม. วารสารวิชาการสำนักงานสาธารณสุขจังหวัดมหาสารคาม [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2563 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 29 ก.พ. 2567];4(8):1-12. สืบค้นจาก: https://thaidj.org/index.php/AJMP/article/view/9512
Asirvatham ES, Ranjan V, Garg C, Sarman CJ, Periasamy M, Yeldandi V, et al. A review of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate associated nephrotoxicity among people living with HIV: burden, risk factors and solutions. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health. 2024;25:101462. doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2023.101462.
ใกล้รุ่ง สุทธารักษ์. อุบัติการณ์การเกิดพิษต่อไตในผู้ป่วยเอชไอวีที่ใช้ยา Tenofovir โรงพยาบาลพระนารายณ์มหาราช. โรงพยาบาลสิงห์บุรีเวชสาร [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2562 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 29 ก.พ.2567];28(1 suppl 1):29-40. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/shj/article/view/256920/
ชุลีกร ปรีชาวิบูลย์, ขวัญดาว ศิลาทอง, พนิดา อยู่เพ็ชร. การศึกษาอาการอันไม่พึงประสงค์ต่อไตในผู้ป่วยติดเชื้อเอชไอวีที่ได้รับยา Tenofovir ร่วมกับ NNRTIs เทียบกับ Tenofovir ร่วมกับ Protease Inhibitors ในโรงพยาบาลราชวิถี. วารสารกรมการแพทย์. 2557;41(5):91–8.
เชิดชัย สุนทรภาส, ภิรุญ มุตสิกพันธ์, รัชฎาพร สุนทรภาส. ปัจจัยเสี่ยงของความเป็นพิษต่อไตในผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับยาทีโนโฟเวียร์ ไดโซพรอกซิล ฟูมาเรท ณ โรงพยาบาลตติยภูมิขั้นสูง. วารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2566 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 29 ก.พ. 2567];33(2):102-11. สืบค้นจาก: https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/TJHP/article/view/261514
ประภาพร เป็งธินา. อุบัติการณ์และปัจจัยเสี่ยงของการเกิดความผิดปกติของไตในผู้ติดเชื้อเอชไอวีที่ได้รับยา Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) [วิทยานิพนธ์เภสัชศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต]. เชียงใหม่: คณะเภสัชศาสตร์มหาวิทยาลัยเชียงใหม่; 2555.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Health Administration Division, Office of the Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Public Health and The Society of Hospital Pharmacist, Ministry of Public Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสารเภสัชกรรมคลินิกอย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และ ชมรมเภสัชกรโรงพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข และบุคลากรในกองฯ หรือ ชมรมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ



